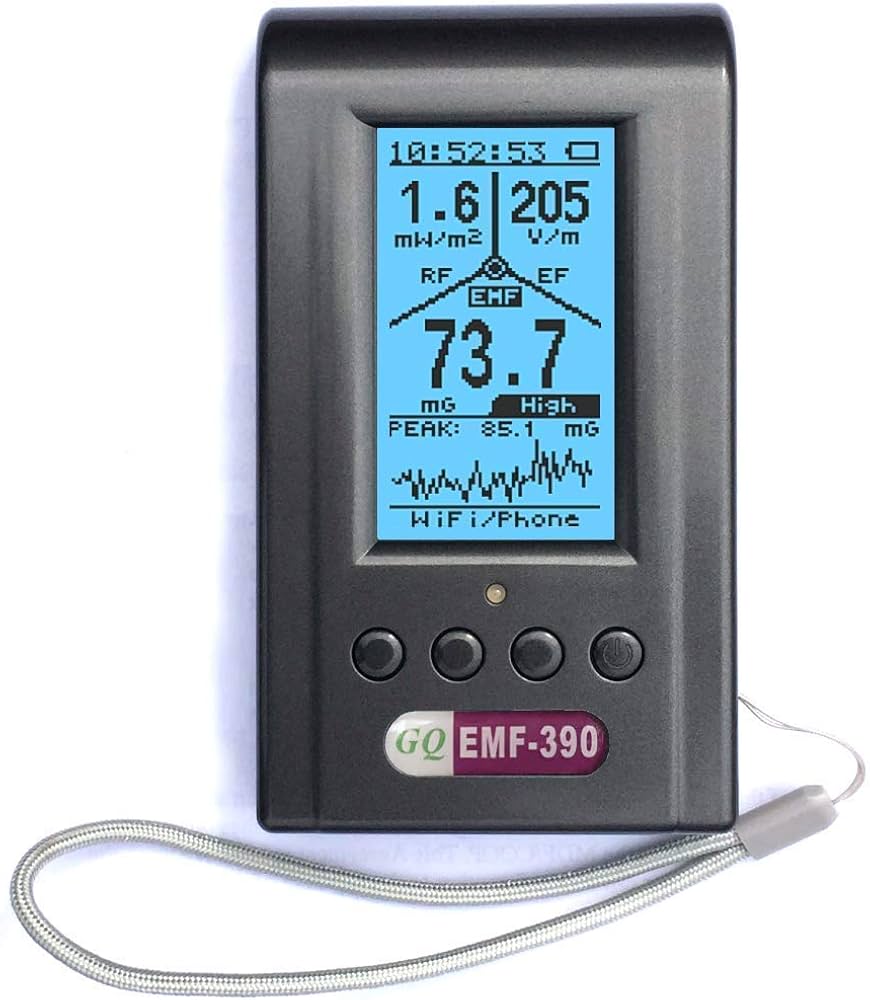
RF Signal Detectors: A Complete Guide to Identifying Wireless Sources and Exposure Levels
Radiofrequency fields come from countless everyday technologies—Wi-Fi routers, smartphones, 5G towers, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, IoT appliances, smart meters, gaming systems, and more. These signals overlap constantly, creating environments where multiple RF sources compete for space. To quickly locate these sources and understand their relative strength, EMF assessors and home users rely on RF Signal Detectors, lightweight tools designed to reveal when wireless activity is present and how intense it is.
RF Signal Detectors do not provide full frequency analysis like spectrum analyzers, nor do they offer broad logarithmic displays like broadband RF meters. Instead, they excel as fast, intuitive detection tools that alert users to the presence of RF energy. For an overview of all EMF testing tools, visit:
https://frequencyblockers.com/emf-testing-tools/
What RF Signal Detectors Measure
RF Signal Detectors sense radiofrequency emissions across a broad range—typically from hundreds of MHz up through several GHz. They detect:
- Wi-Fi signals (2.4 GHz / 5 GHz / 6 GHz depending on model)
- Cellular transmissions (4G, 5G sub-6 GHz)
- Bluetooth activity
- Microwave leakage
- Smart meter bursts
- Cordless phone transmissions
- Wireless cameras and baby monitors
- IoT device chatter
- Radar-based automation systems
Key measurable indicators include:
- Presence of RF energy
- Relative signal intensity
- Pulsing behavior
- Directionality (on some models)
- Audible patterns that correlate with specific signal types
Most RF Signal Detectors convert RF activity into visual bars, lights, vibration alerts, or audio patterns.
Why RF Signal Detectors Are Essential for EMF Diagnostics
1. Fastest Tool for Locating RF Sources
They instantly show whether a wireless device is transmitting and how strongly.
2. Ideal for Non-Technical Users
Unlike analyzers or broadband meters, RF Signal Detectors are simple and intuitive.
3. Reveal Hidden or Unexpected Transmitters
Common surprises include:
- Smart TVs broadcasting even when “off”
- IoT hubs inside appliances
- Wireless speakers
- Smart lights or thermostats
- Hidden cameras (in rare cases)
4. Excellent for Apartment & High-Density Environments
Multiple units above, below, and beside can contribute to exposure—RF Signal Detectors help identify which direction signals come from.
5. Perfect for Quick Scans
Consultants use them during initial walkthroughs before deeper analysis.
6. Extremely Helpful for Smart Meter Verification
They reveal burst frequency and proximity strength.
How RF Signal Detectors Work
RF Signal Detectors contain:
1. Wideband Antenna
Picks up RF signals across a broad spectrum.
2. RF Detection Circuitry
Rectifies incoming RF energy into a measurable voltage.
3. Strength Indicator
Displays intensity using:
- LEDs
- Bar graphs
- Audible indicators
- Digital readouts
4. Filtering Components
Some models filter out very low or very high ranges depending on use case.
These detectors do not reveal exact frequency, only the presence and relative strength of RF activity.
Applications for RF Signal Detectors
1. Home EMF Assessments
Identify transmitting sources such as:
- Routers
- Smart TVs
- Baby monitors
- Bluetooth devices
- Smart appliances
2. Office & Workplace Testing
Reveal RF intensity near:
- Copy centers
- Conference rooms
- Wi-Fi-dense environments
3. Smart Meter Location & Burst Timing
RF Signal Detectors clearly capture the pulsing signature of smart meters.
4. Vehicle EMF Scans
Detect emissions from:
- Car Wi-Fi
- Onboard Bluetooth
- Radar-based driver-assist systems
5. Travel & Hotels
Quickly assess RF levels in unfamiliar environments.
6. DIY Troubleshooting
Determine whether a specific device is transmitting before making shielding decisions.
How to Use RF Signal Detectors Effectively
1. Hold the Detector at Arm’s Length
Reduces body-based shielding effects.
2. Sweep Slowly
Move the detector through the room, watching for spikes.
3. Turn Devices On and Off
Compare baseline vs. active transmissions.
4. Use Audio Mode (if available)
Many devices produce distinct audio signatures:
- Wi-Fi → rapid pulsing
- Bluetooth → rhythmic bursts
- Smart meters → short intense spikes
5. Test Bedrooms at Night
Wireless transmissions often change after midnight.
6. Move Toward and Away From Suspected Sources
Signal strength changes help pinpoint exact locations.
7. Verify Shielding
Check whether shielding blankets, films, or paints reduce RF levels.
Understanding RF Signal Detector Readings
These detectors usually show relative intensity, not absolute power measurements.
Typical indicator categories include:
| Level | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Very Low | Minimal RF activity |
| Low | Background wireless levels |
| Moderate | Nearby transmitting devices |
| High | Strong RF exposure in immediate area |
| Very High | Close proximity to active transmitter |
For precise exposure metrics (µW/m²), pair RF Signal Detectors with broadband RF meters or HF analyzers.
Types of RF Signal Detectors
1. Basic Pocket-Size Detectors
- LED or bar-graph indicators
- No frequency identification
- Affordable and simple
2. Audio-Signature Detectors
- Translate RF signals into audio patterns
- Very useful for signal identification
3. Directional RF Detectors
- Help locate the direction a signal is coming from
- Useful in complex indoor environments
4. Multi-Band RF Detectors
- Detect common wireless categories separately
- Useful for distinguishing Wi-Fi from cellular or Bluetooth
5. Covert Surveillance RF Detectors
- Used for locating hidden cameras
- Often marketed for security testing
Price Ranges for RF Signal Detectors
| Category | Typical Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | $20–$60 | Quick household checks |
| Mid-Range | $60–$150 | Home EMF assessments |
| Advanced | $150–$350 | Consultants & directional testing |
| Security-Focused | $80–$250 | Hidden device detection |
Even budget detectors offer surprisingly useful insight.
Advantages of RF Signal Detectors
- Immediate feedback
- Very easy to use
- Great for hidden or intermittent RF detection
- Portable and lightweight
- Complement high-tier meters
- Ideal for rapid room-by-room scans
- Affordable entry into RF diagnostics
Limitations of RF Signal Detectors
- Do not show exact frequencies
- Cannot provide power density readings
- May saturate near strong transmitters
- Not suitable for engineering-level analysis
They are best used as fast scanning tools, not final diagnostic instruments.
RF Signal Detectors vs. Broadband RF Meters
| RF Signal Detectors | Broadband RF Meters |
|---|---|
| Show signal presence & intensity | Provide numeric exposure levels |
| Very fast & intuitive | Require interpretation |
| Great for detecting hotspots | Great for quantifying exposure |
| Cannot show frequency | Cannot always identify source |
Most EMF professionals carry both tools.
Common Mistakes When Using RF Signal Detectors
- Standing too close to reflective surfaces
- Holding the detector against the body
- Misinterpreting noise floor fluctuations
- Scanning too quickly
- Ignoring nighttime patterns
- Using detectors with depleted batteries
Slow, steady movements yield the most reliable results.
FAQs About RF Signal Detectors
Do RF Signal Detectors detect 5G?
Yes—any sub-6 GHz 5G is detectable if within scanner range.
Do they detect hidden cameras?
Some models are designed specifically for that purpose.
Are RF Signal Detectors safe?
Yes—they passively receive signals and emit nothing.
Do they replace spectrum analyzers?
No—they complement analyzers by offering fast scanning.
Key Takeaways
- RF Signal Detectors provide fast, intuitive detection of wireless transmissions, making them ideal for locating RF sources and identifying hotspots.
- While they do not offer frequency-specific analysis, they are essential for quick RF diagnostics and for guiding deeper testing with analyzers.
- They are highly portable, affordable, and invaluable as part of a complete EMF toolkit.
- For more EMF testing tools, visit:
https://frequencyblockers.com/emf-testing-tools/
References
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) — RF Measurement Principles
https://www.nist.gov - Frequency Blockers — EMF Testing Tools Overview
https://frequencyblockers.com/emf-testing-tools/